Roots Web Sales Optimisation
Project Overview
Topic: Optimisation of online purchases in Roots Canada
End Date: Dec 2022
Methods: High-Level Heuristic Evaluation, Competitive Analysis, Analytics and Data, A/B Testing, Survey, Comparing New Design with the Old One
Deliverables: Research Plan, Presentation, New Design for A/B testing
Collaboration: 5 UX designers
My role: UX researcher, preparing new design elements for A/B testing
Tools: Illustrator, Google Slides, Canva
Problem Statement
Roots Canada redesigned its website, and online sales have dropped since then, although the number of visitors are same. Roots Canada wants to understand why fewer visitors end up buying online for the next 40-60 days.
Optimisation Goals
- Increase the number of online sales and increase revenue for Roots Canada
- Provide solutions that lower bounce rate
Solution
We prepared a research plan for the client that includes different methods (interviews, usability testing, A/B testing, and survey). In this research plan, we explained why we need to go further analysis with these methods and shared our new design for the problematic screens in checkout for the A/B testing. We determined our research methods by analyzing the competitors and the Roots Canada website through Heuristic Evaluation. The problem did not seem to be device-specific, so the problem was either inside the cart or past the checkout step to the very last step. We worked backward; we started by reviewing the data for the Payment page and went backward to the Cart data. We found some problems related to the new design and prepared alternative screens with new design elements for A/B testing.
Process
Research
Hypotheses
1. The recent redesign of Roots Canada’s buy flow is affecting its online sales.
2. Users feel confused and frustrated while shopping for items on the Roots Canada website.
Research Questions
1. What stops users from completing their task in buying items on the Roots Canada’s website (desktop and mobile)?
2. What factors make users confused during shopping?
Competitive Analysis
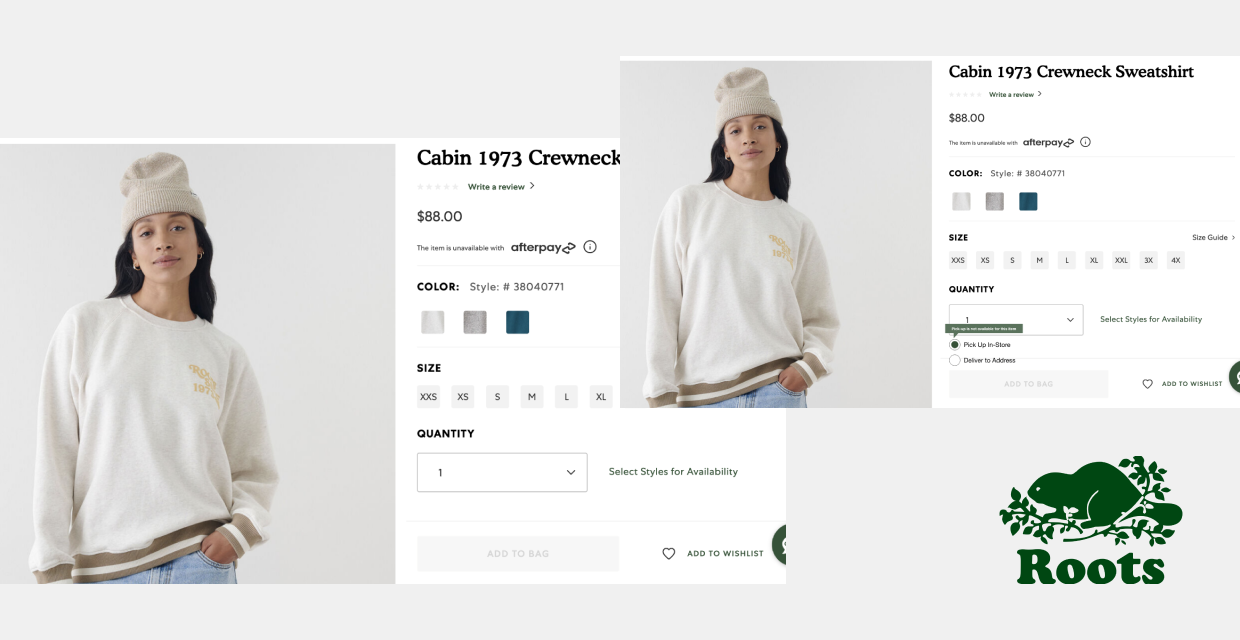
For the competitive analysis, we analyzed Roots Canada’s major competitor: Lululemon (www.lululemon.com)
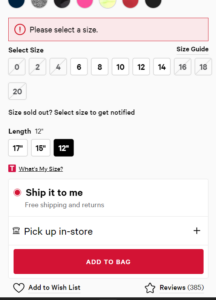
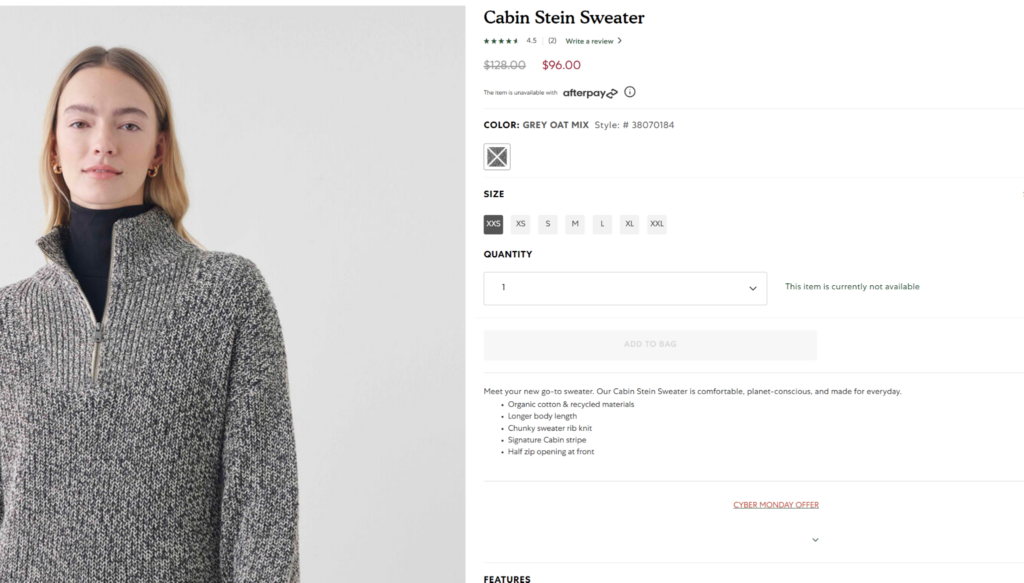
The Lululemon website followed the heuristic “Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors” by clicking the CTA “Add to Bag” button. It provides noticeable feedback that tells the users what to do before an item can be added to the cart. The “Please select a size”warning appears after clicking on “Add to Bag” button if size is not selected.
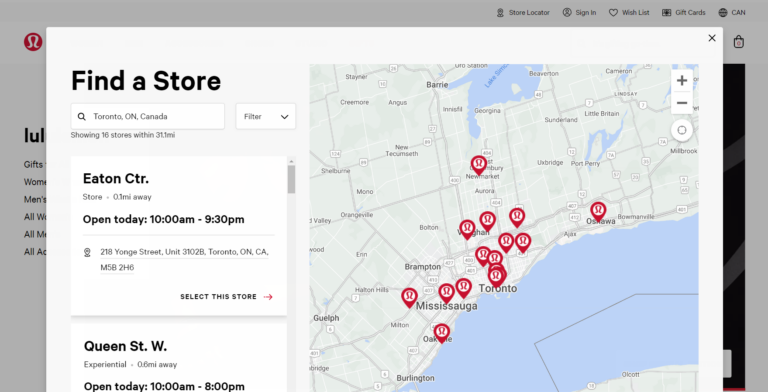
The Lululemon website applied two heuristics successfully for their Store Locator feature.
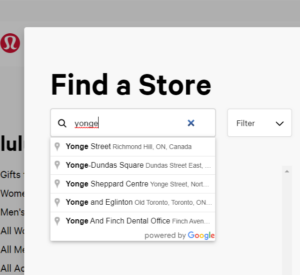
Using the “Recognition rather than recall” heuristic, the site displays suggestions in the search bar as the user starts typing in an address before proceeding to locate the nearest store.
Using the “Flexibility and efficiency of use” heuristic, the “Select This Store” button gives users to conveniently select a store location within the search results.
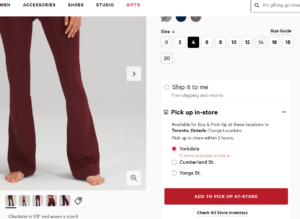
Lululemon’s application of the heuristic “Flexibility and efficiency of use” allows users to choose either pick-up or delivery from the product page of the website itself. This feature also gives users the convenience of seeing the availability of a product across multiple store locations near them.
High-Level Heuristic Evaluation
We conducted a heuristic evaluation with the aim of identifying heuristic issues that greatly affect users’ interaction with the buy flow on the Roots Canada website. We will then synthesize our findings and share with the stakeholders.
Why Heuristic Evaluation?
Conducting a heuristic evaluation will help us identify some of the problems that might be negatively affecting the conversation rate on the Roots Canada’s website. We believe this method will also help us generate test ideas for the testing phase.
Notable Heuristic Evaluation (1/4)
Heuristic Violation – Help users recognize, diagnose, and recover from errors
- Can’t click “Add to Bag” button without selecting the item’s colour and size. Although the site does notify the user to “select styles for availability”, the error message is not very noticeable
- The process of adding an item to the cart on Roots is unfamiliar and confusing to the users. Adding to cart process needs Help and Documentation.
Recommendation: When clicking “Add to Bag” Display an error message when the user tries to click “Add to Bag” and tell them how to fix the error.
Notable Heuristic Evaluation (2/4)
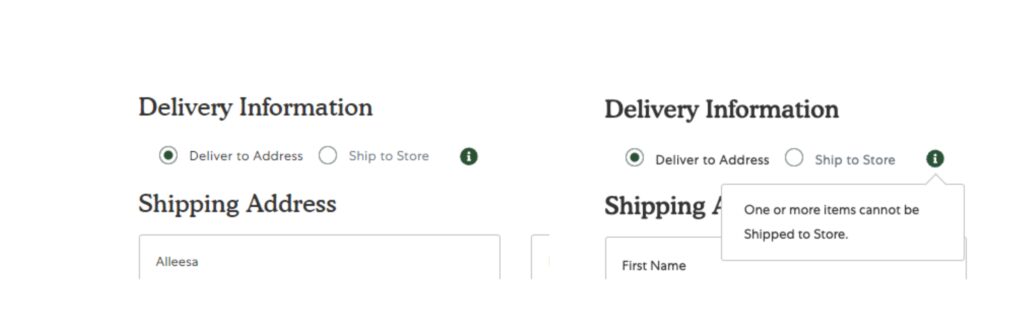
Heuristic Violation – Consistency and standards
- The “Ship to Store” option under Delivery Information in the checkout page is unclear.
- Website navigation and footer disappear on the checkout page
- The “Ship to Store” option is only available depending on the kind of items you have in your cart
Recommendation:
1) Rephrase the labelling to be more clear.
2) Keep the navigation and footer in the checkout page so that users can have access to “Find a Store” button or Store locator on the navigation
3) In product pages, implement a feature where users can see the stock of a product and eligibility for pickup/delivery across multiple nearby stores.
Notable Heuristic Evaluation (3/4)
Heuristic Violation – Flexibility and efficiency of use
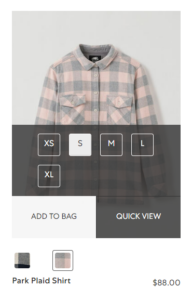
Items aren’t added to the cart once a size is selected. For a user to add an item to their cart they must click “Add to bag”, select a size, and then click the button again. The indication of having to press the “Add to Bag” button a second time is unclear (i.e. button turns white after choosing size).
Recommendation: Have the item be added automatically to the cart when the user picks a size. Provide visual feedback when an item is added.
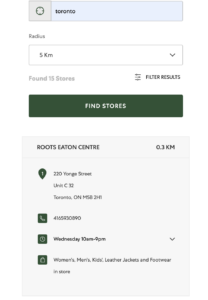
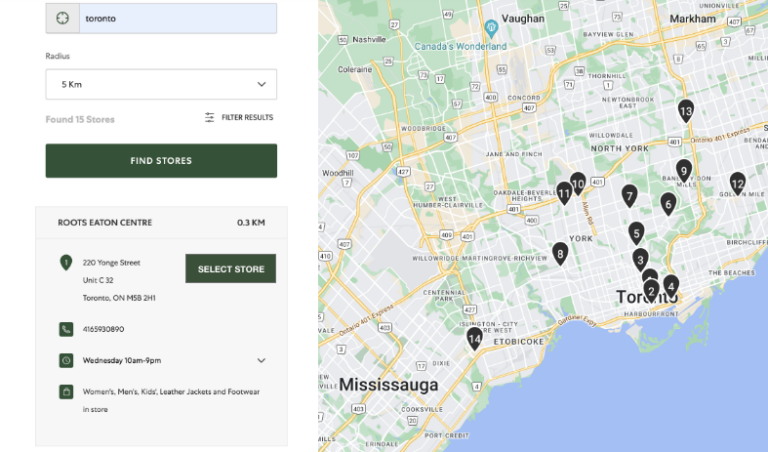
The user can only select the store by clicking on the pins on the map after searching a location in the Store Locator.
Recommendation: Make the process efficient by adding a “Select Store” button to the listed stores when search results appear in the Store Locator.
Notable Heuristic Evaluation (4/4)
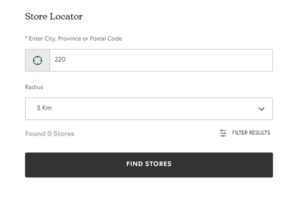
Heuristic Violation – Recognition rather than recall
The user has to rely on memory while typing in the desired address in the Store Locator.
Recommendation: Add a feature to the search bar where suggestions are shown as the user types in the address
What Works Well (1/2)
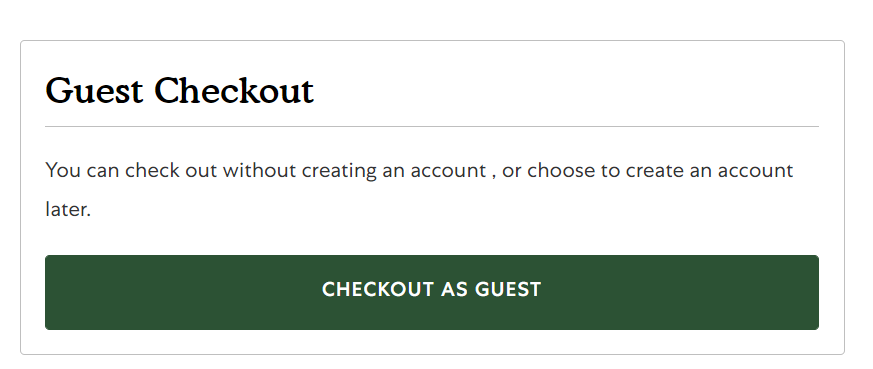
Heuristic – Flexibility and efficiency of use
Provides users/customers an option to checkout as a guest.
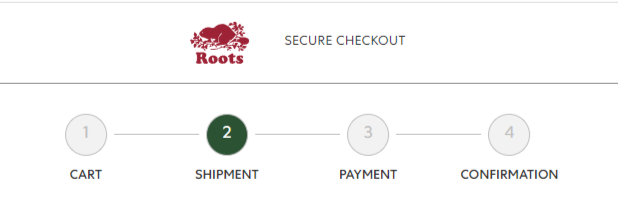
Heuristic – Visibility of system status
Interface has design elements that lets the users know what stage/step they are in the checkout page
What Works Well (2/2)
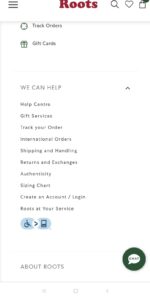
Heuristic – Aesthetic and minimalist design
Website has an accessibility option that makes the website accessible to people with disabilities
Website follows the five standards of AODA
Why A/B Testing?
Using the A/B testing method will allow us to compare two different designs simultaneously – this way, we can observe which design is easier to understand and keeps users in the buy flow from the outcome of the design with the highest conversion rate. Also, since Roots Canada would like this issue to be resolved as soon as possible, a quicker method is needed. A/B testing only requires 3 days to complete, which is a much shorter period of time compared to other methods.
A/B Testing
After completing a competitive analysis and conducting a heuristic evaluation, we will proceed with A/B testing. The software that will be used to conduct the A/B testing is Optimizely. These are the design elements we have recommended to test:
- Comparing “Add to Bag” button to “Add to Cart” button
- Check “Ship to Store” to “Pickup” in checkout
- Adding a pop-up notification that tell users to select item specification before clicking on “Add to Bag” button, when the “Add to Bag” button is clicked on
- Add search suggestions under the search bar in the Store Locator page
A/B Testing Ideas
1) Comparing “Add to Bag” button to “Add to Cart” button
A
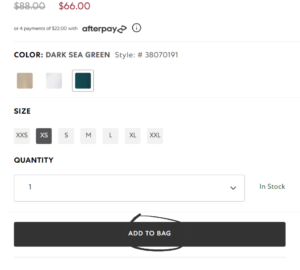
B
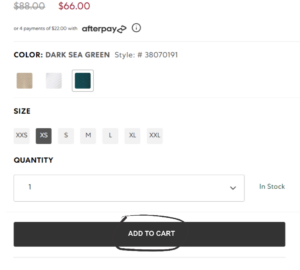
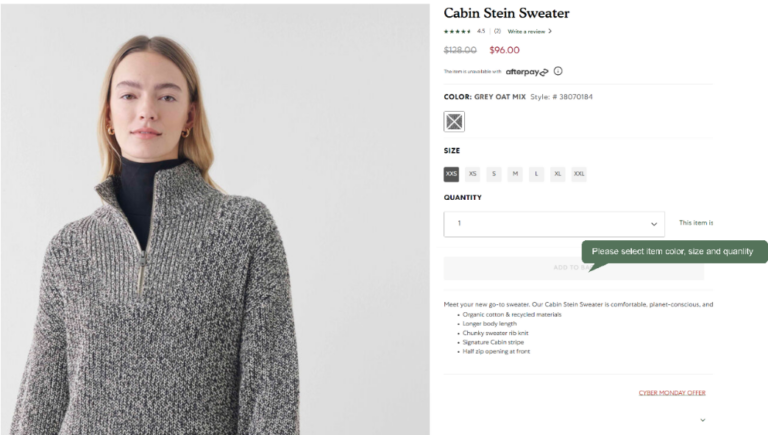
2) Display an error message when the user tries to click “Add to Bag” and tell them how to fix the error before adding Item to bag.
A
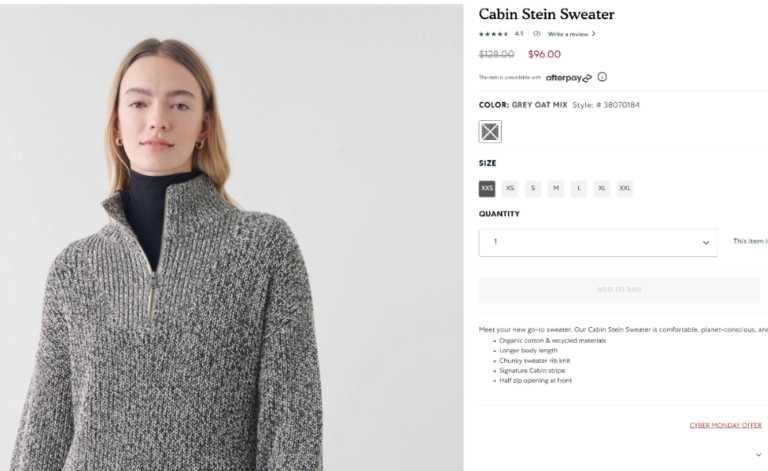
B
3) Add a “Pick Up In-Store” and “Deliver to Address” radio buttons to the product page, and display an error message that is saying “item is not available for pick-up” when the user clicks “Pick Up In-Store”, and the item is not available for pick-up.
A
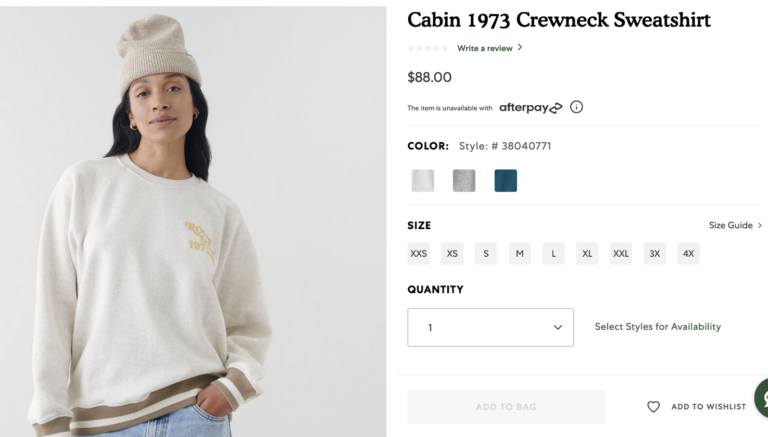
B
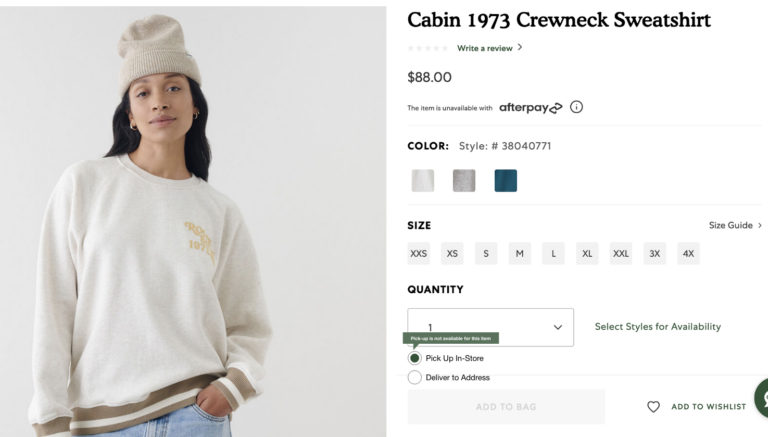
A
4) Change “Ship to Store” to “Pickup” in checkout
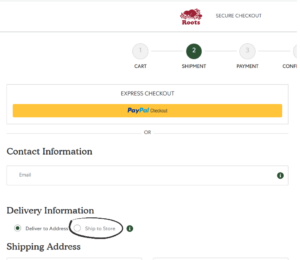
B
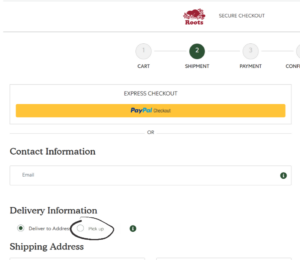
5) Add navigation to Checkout page
A
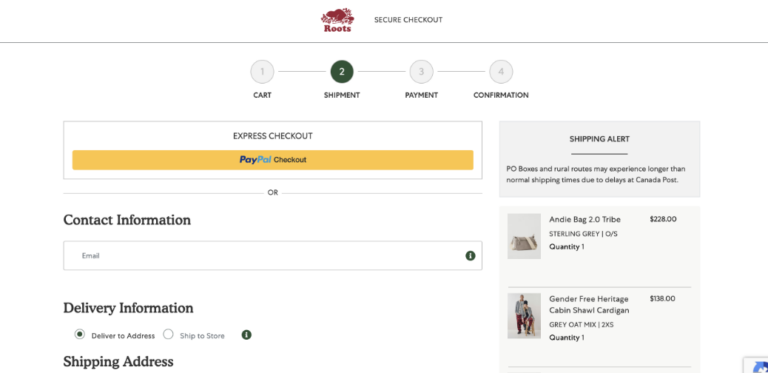
B
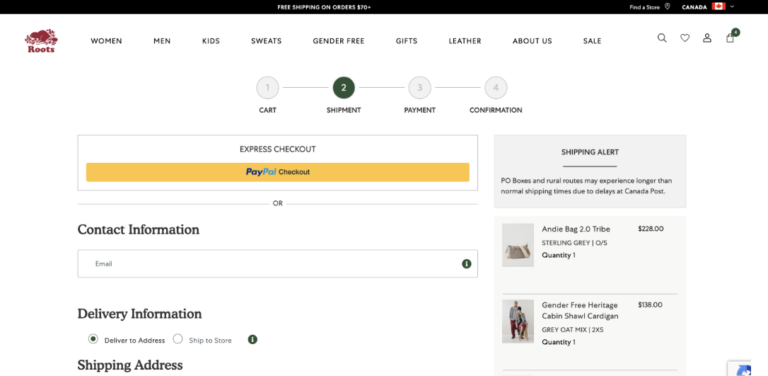
6) Add search suggestions under the search bar in the Store Locator page
A
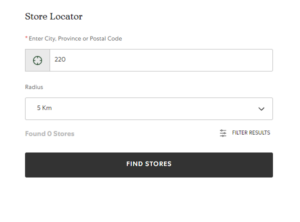
B
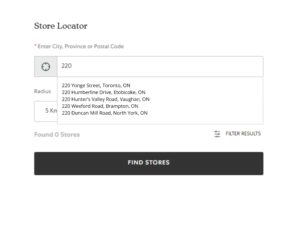
7) Add Select Store button to the stores found with the Store Locator
A
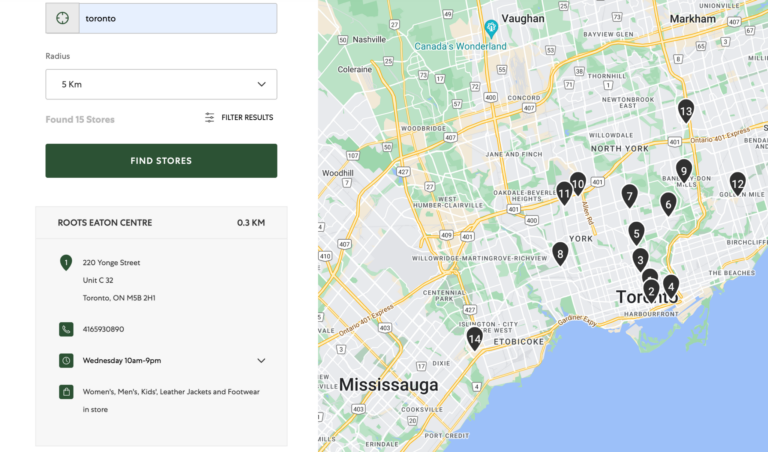
B
Research Plan Will Be Presented To The Client
Team Roles and Responsibilities
Design and Research Team
UX Researcher
- Develop research plan
Conduct research and identify issues in the Roots Canada website buy flow - Report to project manager
Project Manager
- Gives feedback on research plan
- Monitor the optimisation project’s progress
- Assure the project is on schedule and meets deadlines
Client
- Review deliverables and give timely feedback
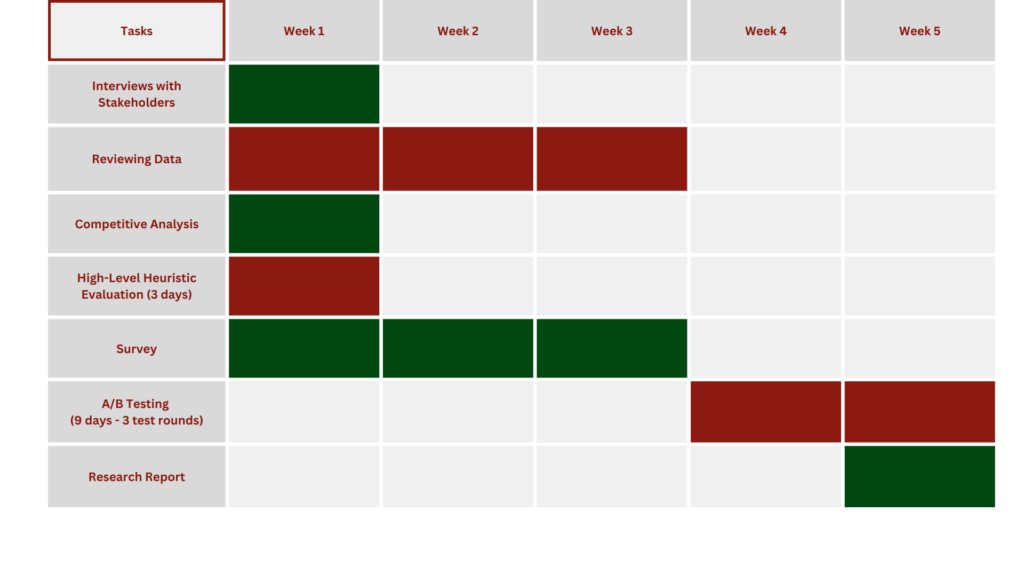
Schedule
Research Methods -
In addition to Competitive Analysis and Heuristic Evaluation
Rewieving Data
We will consult with the data science team to validate the research done during the heuristics evaluation and competitor analysis. The primary software that will be used for this method is Google Analytics. Also, we will take a look at the website data from the past 3 months to see what factors could have affected the decrease in online sales.
We will focus on the following data:
- Average session duration
- How many minutes on specific pages
- Which pages the users generally go to
- Ratio of new to returning visitors
- Bounce rate – the percentage of visitors that leave a webpage without making a purchase
Comparing New Design with the Old One
After reviewing the data, we will compare the new design of Roots Canada with the old one and see if we can match some broken data points with some major changes in design that could explain the drop-off.
Survey
After we identified specific steps where people abandon, we will add the survey there, and only present it to the people who abandon without continuing the next step.
Assumptions, Risks, & Mitigations
Assumptions
- Data science team is available
- The Roots Canada website is functional and available
- All research is collected
- Found reasonable number of target people to do the A/B testing.
Risks
- A/B testing software not giving accurate data and results
- Website having multiple bugs posing to be an hindrance towards A/B testing
- Technological issues and complications with A/B testing
Mitigations
- Check if the software and relevant technology is working prior to testing
- Ensure that the website is bug free and debugged prior to testing
- Provide backup software for A/B testing
Next Steps
- We would run a few A/B tests and find out if we are noticing an improvement in conversion for that step (e.g. more people moving to the next step)
- In the event that we are noticing an improvement (5-10% increase), we would implement the new change in production (tests are live, but once the test is paused, the change is no longer live. Implementing a permanent change in production is needed.
- We would repeat with more tests until we are back to normal (same amount of sales as before the re-design exercise) – this could take up to 12 months, depending on the magnitude of the problem
- We would be inclined to improve conversion via multiple A/B tests inside the buy flow before conducting a usability test based on some new design
- In the event that we come across multiple problems during our analysis, we could consider to re-design the buy flow and conducting some usability tests using the new flow